Dutch Automotive History (part 53) Riley, Reliant, Reo, Rosengart (96 photos)
Riley (Coventry, UK, 1898-1969)
To ensure a prosperous existence for his four sons, William Riley left textile production in 1890 and bought the Bonnick bicycle company. In 1896 it was renamed the Riley Cycle Company Limited. There, young Percy Riley built the first car with a single-cylinder engine equipped with a positive intake valve drive. All engine parts were made by hand, including cutting the teeth of the transmission gears. The machine turned out to be quite efficient, but was never put into production.
In 1900, a lightweight three-wheeled motorized carriage, the Royal Riley, was born with a De Dion-Buton engine, two front steered wheels and a rear drive wheel. In 1904, a second car was built, the engine for which was designed by Percy Riley, and assembled by the Riley Engine Company, founded by the remaining sons of William Riley. This car was produced until 1907. Back in 1905, based on the “three-wheeler,” Percy Riley developed a 4-wheeled model, using the same engine and a new gearbox. All Riley cars were equipped with lightweight wheels with spokes and a central fastening nut. Wheels soon became a profitable product. They were bought by many automobile companies.
In 1907, Riley released a 5-seater 12/18HP car with a front-mounted V2 engine with a displacement of 2035 cm3. In 1909, the “1ONP” model appeared with a 1390 cm3 V2 engine designed by Stanley Riley. In 1911, the Riley Cycle Company ceased production of bicycles and was renamed Riley Limited, Coventry. Since William Riley preferred to produce only automobile wheels, his sons founded a new enterprise, Riley Motor Manufacturing Company, in 1912 to produce automobiles.
The first was the 17HP model with a 4-cylinder engine with a displacement of 2932 cm3, shown at the 1913 London Motor Show. At the same time, brothers Victor and Stanley opened another company, Nero Engine Company, which produced the 10HP model with an engine with a displacement of 1096 cm3. However, its production had to be interrupted with the outbreak of the First World War. All enterprises of the Riley family switched to the production of ammunition. In 1914, a factory in Foleshill, near Coventry, fell into their hands. It was he who, after the end of the war, became the base for the reorganization of the Riley group, and since 1919, its main production center. That same year, Riley Limited ceased production of wheels and merged with the Nero Company. At the same time, Riley Motor Manufacturing completed production of the chassis and concentrated its efforts on the manufacture of bodies, receiving the name Midland Motor Body Company. Well, the Riley Engine Company began assembling the Riley-17/3ONR models at the old production facilities.
In 1919, Riley Limited released the 10.8HP model, equipped with a 35-horsepower, 1498 cm3 engine with side valves. In 1923, its sports version, Redwing, appeared. At first, Percy Riley decided to devote himself to the construction of stationary and marine engines, so the Riley Engine company appeared in the automotive sector only in 1926, introducing the quite successful 9HP, or Nine, with an engine displacement of 1087 cm3, having an overhead camshaft and hemispherical combustion chambers. The Riley Limited company redesigned the engine of its 10.8HP, using a Ricardo cylinder head, also with hemispherical combustion chambers. The new car began to be called "11/40HP", but in 1928 its production was discontinued. Meanwhile, the Riley Engine Company introduced three new variants of the Nain model: the Kestrel sedan, the Brooklands sports car and the Monaco - one of the first cars with an accessible trunk. from the salon. In 1929, under the designation “14.6HP”, a version of the “Nain” model appeared with a 6-cylinder engine with a displacement of 1633 cm3.
To simplify the complex interactions between related firms, Riley Limited assumed overall management of the Riley Engine and Midland companies in 1931. In the 1930s, the Riley program was replenished with numerous variants of existing models with 4- and 6-cylinder engines. The most famous among them were the Falcon sedan with an aerodynamic body and numerous sports cars: Gamecock, Imp, Sprite, Lynx. The main place was occupied by the prestigious two-seater roadster "MRN", produced in small quantities in 1934-1935. In 1935, Riley produced several examples of a more powerful and spacious 8/90 car with a 2.2-liter V8 engine.
In the mid-30s, the company began to be plagued by serious financial difficulties. In 1938
Then it became the property of the Nuffield concern. Only three sedans with 4-cylinder engines with a displacement of 1496 and 2443 cm3 remained in the program. They were also produced under the designation "RM" after the Second World War (until 1953). In 1948, the cars received independent front wheel suspension and updated bodies. In 1952, Riley became part of the new British concern British Motor Corporation.
The high quality of the 1.5- and 2.5-liter Riley engines, developed back in 1926, made it possible to install them in 1953 on new sedans and sports cars of the RME and Pathfinder series. Only in 1957 they were replaced by a new 6-cylinder power unit with a displacement of 2639 cm3 from the Austin car. In the same year, the last original Riley 1.5L appeared - a light sedan with a 1.5-liter engine. Then the unification of Riley products with machines from other companies included in the concern began.
RELIANT (Tamworth, UK, 1935-)
When the small company Raleigh stopped producing the Safety Seven three-wheeled passenger car in 1935, one of its creators, T. L. Williams, founded his own company, Reliant. He re-launched this simple two-seater model with a single front wheel. Such extremely simple cars were cheap and taxed like motorcycles, so the demand for them was constantly increasing. Since 1939, Reliant began to equip its “three-wheelers” with an engine from an Austin Seven passenger car. After the war, the UK retained tax incentives for vehicles weighing less than 406 kg. This allowed Reliant in 1952 to begin production of a new three-wheeled vehicle, the Regal, with a 4-cylinder engine with a displacement of 748 cm3, capable of carrying two or four people. Subsequently, it was equipped with engines of 598 and 70 cm3 and was offered until the early 70s. In 1969, Reliant was acquired by Bond Cars, which also specialized in the production of three-wheeled cars. As a result, the three-wheeled Bond Bug with a more modern wedge-shaped body appeared on the market. The last mass-produced three-wheeled car in 1973 was the Robin, with a fiberglass body. Since 1982, at the request of lovers of these unique cars, Rilient introduced the miniature Rialto.
Since the mid-50s, the demand for “three-wheelers” began to fall sharply, so the management of Reliant decided to switch to regular four-wheeled cars. The first of them appeared in 1961. It was a light sports Saber with a plastic body and a 4-cylinder engine from the Ford Consul model with a displacement of 1703 cm3. The first attempt was unsuccessful: the Saber was unreliable and unstable, especially on wet roads. It is known only for the fact that it was collected under license in Israel. In 1963, the new Saber Six received a 2553 cm3 6-cylinder engine from the Ford Zephyr model.
The direct successors of three-wheeled cars in 1964 were four-wheeled minicars "Rebel" with an engine displacement of 598 cm3, which in 1967 was increased to 362,750 cm3. In 1975, Reliant released the four-wheeled Kitten with a cargo-passenger body. In 1982, the miniature universal Fox appeared.
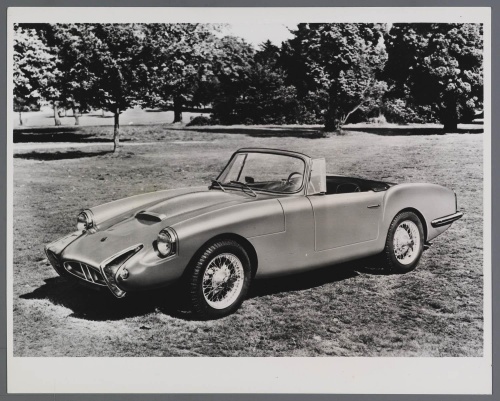
In 1964, "Reliant" boldly declared itself in the class of quite prestigious sports cars. The first of these was the sports Scimitar, followed in 1968 by the very unusual Scimitar GTE, the body of which combined the advantages of a sports coupe and a utility station wagon. In 1984, the elegant two-seater sports car "Simiter SS-1" appeared with a fiberglass body and a 1.3-liter Ford Escort engine, to which a 1.6-liter unit with 96 hp was soon added. In 1985, Reliant, in agreement with Ford, began assembling a powerful two-seater rally car, the Escort RS-200.
Things have never been easy for a small, independent company. In 1996, Reliant declared bankruptcy. However, the company found rich sponsors and was revived again. Now it produces only sports convertibles "Simiter Saber" with "Rover" engines with a displacement of 1.4-2.0 liters.
REO (Lansing, USA, 1904-1936)
Ransom Eli Olds, founder and owner of Oldsmobile, is considered one of the founders of mass production technology for automobiles. Satisfied with his achievements, in 1904, 40-year-old Olds left his own company, deciding to retire. But he was not left alone: several American entrepreneurs persuaded Olds to take over the leadership of the new company, giving him a 52 percent stake and the right to make all decisions independently.
The new company, named RIO after Olds' initials (REO - "Ar-I-Oy"), began producing cars with single-cylinder engines in 1904.
lyami. In the first year there were enough buyers for them. The proceeds went towards the development of a car with a 2-cylinder engine. In 1906, a model with a 4-cylinder power unit entered the market, but it did not attract much interest. Failure did not discourage Olds, and in 1911 the company released a new machine called the Fifth.
In 1920, the production program included only one Model T with a 6-cylinder engine and magneto ignition. The rear axle was mounted on two springs installed underneath it. The features of the car include two independent braking systems, driven by two different pedals, and the absence of a hand brake. In 1927, this model was replaced by the new Flying Cloud with an 85 hp engine. It was a great success, and the company managed to sell a record number of cars in a year - 29 thousand units. In 1931, the Flying Cloud Eight and Custom Royal Eight models with 8-cylinder engines appeared. Two years later, one of the first in the United States, RIO tested and launched a 2-speed semi-automatic transmission. The driver controlled it using a lever on the instrument panel, which also included reverse gear. In 1936, a 4-speed automatic transmission appeared. By this time, RIO was on the verge of bankruptcy and soon stopped producing passenger cars. For another 30 years she was engaged in the production of trucks.
Ransom Eli Olds died in 1950 at the age of 86. He was not only an outstanding automobile designer, but also the inventor of America's first functional grain combine.
ROSENGART (Neuilly, France, 1928-1955)
Lucien Rosengard became famous in the early 1920s when he founded the Society for the Development of the French Automotive Industry (SADIF). It played a big role in the formation of the Citroen company, saving it from financial collapse by providing a large loan that covered the cost of cars that had not yet been sold. Thanks to this, Citroen was able to develop new cars and organize their mass production. Having secured strong connections among large automobile industrialists, Rosengar received the post of technical director at Peugeot, and in the late 20s he founded his own business.
The first passenger car "Rosen-rap-LR-2" with a 4-cylinder engine with a displacement of 747 cm3 was presented at the 1928 Paris Motor Show. It was a variant of the famous British car "Austin Seven", for which Rosengar bought a license. The car differed from the original only in its external design. For example, the radiator trim had a chrome transverse trim, fashionable in France. In 1930, an improved version of the LR-4 appeared, and then an extended LR-44, which served as the basis for the new LR-62 car with a compact 6-cylinder Austin engine with a displacement of 1097 cm3.
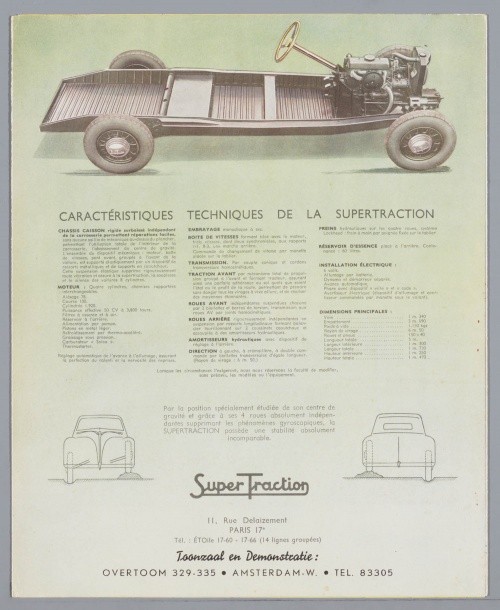
In 1932, Rosengar acquired the rights to produce the Adler Trumpf front-wheel drive car and began assembling it. The first version differed from the German one only in the emblem. A year later, the car was modernized, it received the index “LR-500” and the name “Supertraction-G”, although in appearance it still resembled its predecessor. In 1934, at the Paris Motor Show, Rosengar presented a new modification with an aerodynamic body, however until 1936, buyers could only purchase options with characteristic angular bodies. At the same time, on the basis of the Austin Seven, production of the LR-4N2 model continued. The LR-4R modification was equipped with a front independent suspension. The best creation of Rosengar was the front-wheel drive " LR-539 SuperTraksion-M" on the Citroen-11BL chassis, with a unique aerodynamic two-door body, which appeared in the spring of 1939.
Soon after the war, Rosengar decided to produce front-wheel drive cars of a higher class. Buyers were offered the Supertrahuit model with an 8-cylinder 3.9-liter Mercury engine, but in those difficult times the expensive car was not in demand. Returning to the old Austin Seven design, Rosengar in 1952 introduced two compact models, the Artisane and the Ariette, with an engine displacement of 747 cm3. Two years later, the Sagaie model appeared with a 2-cylinder overhead-valve opposed Panhard Dyna engine of 850 cm3 with air cooling, which allowed a maximum speed of up to 120 km/h. Unable to compete with the Renault and Panhard models, Rosengar ceased operations in 1955.


























К сожалению, к данной новости архивы недоступны для скачивания

